How Metabolic Procedures Can Help Control Diabetes, Blood Pressure, and Other Chronic Diseases?
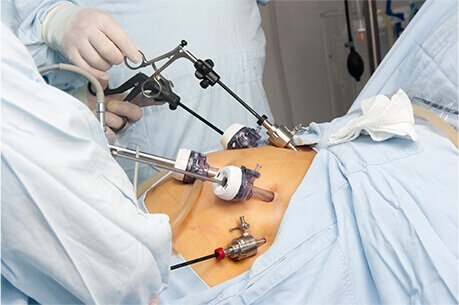
Metabolic surgery is a proven and credible option for individuals struggling with obesity and its associated health complications. By modifying the stomach and intestines through minimally invasive laparoscopic or robotic techniques, this procedure promotes significant weight loss while effectively addressing chronic conditions such as uncontrolled diabetes (despite being on medical treatment), hypertension, sleep apnea, and high cholesterol.
Compared to traditional methods, patients undergoing minimally invasive metabolic surgery, benefit from reduced discomfort, shorter hospital stays, and faster recovery times. Importantly, metabolic surgery is, at times, considered even safer than common procedures like gallbladder removal or hip replacement.
Beyond weight management, this transformative treatment enhances overall well-being, extends life expectancy, and significantly reduces the risk of future health issues.
How Metabolic Surgery is Different from Bariatric Surgery?
Metabolic surgery offers a promising approach to effectively managing uncontrolled type 2 diabetes, leading to significant improvement of the disease. While currently synonymous with weight-loss surgery, metabolic surgery tends to focus on more targeted interventions that affect the body’s metabolism whereas bariatric surgery, mainly focused on weight loss, alters the digestive system through procedures like gastric bypass or sleeve gastrectomy. These interventions primarily aim to reduce food intake or limit nutrient absorption, resulting in weight loss.
Types of Metabolic Surgery for Diabetes
Metabolic surgery has demonstrated remarkable efficacy in managing diabetes. A vast majority of patients experience significant improvements within days of the procedure, characterized by lower blood sugar levels and reduced reliance on diabetes medications.
Notably, an impressive 78% of patients achieve diabetes remission, and better glycemic control, at times eliminating the need for medication.
There are several metabolic surgical approaches, of which commonly used are as follows:
- Sleeve Gastrectomy with Duodenojejunal Bypass (SDJB): Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy with duodenojejunal bypass (LSG-DJB) has been designated as a novel metabolic surgery procedure. This combination of sleeve gastrectomy and proximal intestinal bypass theoretically offers an effective and prolonged anti-diabetes effect.
- Sleeve Gastrectomy with Proximal Jejunal Bypass (SG-PJB): This is a surgical weight-loss procedure that modifies the digestive system to improve metabolic health. By reducing stomach size and bypassing a portion of the small intestine, it alters the body’s processing of food and nutrients, leading to significant weight loss and improved control of conditions like type 2 diabetes.
- Ileal interposition: It is a metabolic surgery that modifies the stomach, duodenum, and small intestine. It’s used to treat type 2 diabetes, especially for achieving diabetes remission, even in patients without obesity. The procedure works by altering the digestive process, which impacts hormone levels and blood sugar control.
By altering the digestive system, metabolic surgery not only reduces food intake and calorie absorption but also directly impacts blood sugar control. Additional benefits include lesser food consumption, increased satiety, and improved weight management.
Mechanism of Action: Facilitating Better Glycaemic Control
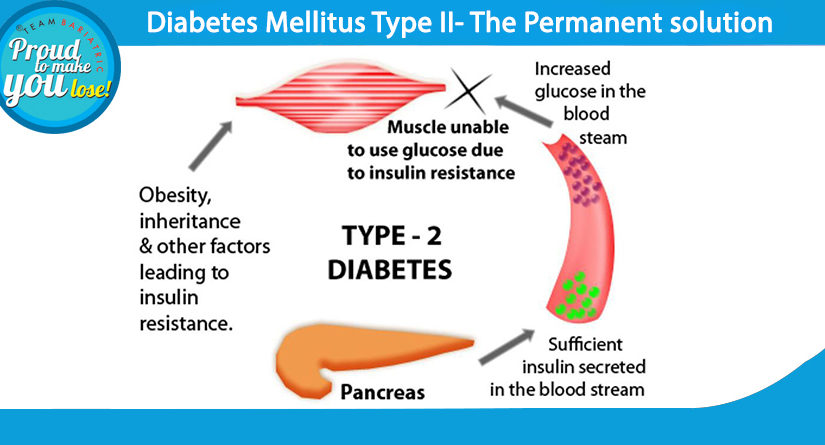
Metabolic surgery benefits blood sugar control in two significant ways.
First, weight loss, an intended outcome of the surgery, improves the body’s ability to use insulin, particularly in muscles and fat.
Second, the surgery itself directly impacts how the body handles food. It changes gut hormones and improves liver function, often leading to better blood sugar levels even before significant weight loss.
Benefits of Metabolic Surgery for People with Diabetes
Metabolic surgery is emerging as an effective alternative for the management of severe obesity and type 2 diabetes. By altering the digestive system, it significantly improves blood sugar control, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels.
It’s essential to monitor patients with existing diabetes-related issues as good glycemic control helps in moderating micro- and macro-vascular complications associated with the eye, nerve, or foot. Additionally, while promising cost-saving potential exists, especially for patients with severe diabetes complications, more studies are required to confirm these economic advantages.
Overall, metabolic surgery offers substantial hope for people with type 2 diabetes, but ongoing research is crucial to fully realize its potential and address potential challenges.
Comparative Effectiveness: Surgery vs. Medical Management
The management of type 2 diabetes has evolved significantly. Traditionally, lifestyle modifications such as diet, exercise, and weight management have been, and still are, cornerstones of treatment. These approaches remain crucial in preventing and managing the condition. However, the complexity of diabetes often necessitates additional interventions.
Medical advancements have introduced a range of medications that effectively control blood sugar levels. These drugs, when used in conjunction with lifestyle changes, can significantly improve diabetes management for many individuals. In some cases, despite optimal medical therapy, diabetes may persist or worsen. Metabolic surgery has emerged as a powerful tool in addressing these challenges. This surgical approach not only induces substantial weight loss but also has a profound impact on metabolic processes, often leading to remission of type 2 diabetes. Metabolic surgery can also be performed on people with normal weight, though, uncontrolled diabetics. In this subset of the population, patients don’t lose weight but get other metabolic benefits from surgery.
It’s important to emphasize that metabolic surgery is not a standalone solution. It complements other treatment modalities. The most effective approach to diabetes management often involves a personalized combination of lifestyle changes, medication, and, in select cases, surgical intervention.
Patient Success Stories and Testimonials
Mr. Jagmeet Kohli, who previously weighed 124.9 kg and had a BMI of 41.3, faced serious health issues including diabetes (with an HbA1c of 10.9) and hypertension. Despite trying to lose weight through diet, he saw little success.
In 2013, he opted for bariatric surgery, and within six months, he shed 37.5 kg. This significant weight loss led to a dramatic improvement in his HbA1c, reducing it to 5.3, and his hypertension was effectively managed. Today, Mr. Kohli is delighted with his results, which have enabled him to excel in both his business and family life. As a testament to his remarkable transformation, he recently walked the runway for the prestigious clothing brand ZARA—a truly impressive achievement!
Choosing the Right Surgeon and the Center
The success of your surgery depends on the expertise of your chosen surgeon and his team. A top-tier metabolic surgery center offers a comprehensive approach, from pre-operative evaluation to post-operative care.
Key factors to consider when selecting a metabolic surgeon and clinic:
- Comprehensive Care: Look for a center that provides a full range of services, including expert surgical care, nutritional guidance, and ongoing support.
- Experienced Team: A dedicated team of specialists, including a metabolic surgeon, bariatric nurse, bariatric dietitian, and program coordinators and program manager, is essential for optimal outcomes.
- Accreditation and Qualifications: Check the accreditation of the clinic and surgeon also look for his qualifications and experience in performing metabolic surgery.
- Proven Success: Research the surgeon’s success rates and patient testimonials to gauge their expertise because patient satisfaction is of paramount importance.
By carefully evaluating these factors, you can increase your chances of achieving successful and long-lasting weight loss through metabolic surgery.
Future Directions in Metabolic Surgery
Metabolic surgery is a proven treatment for severe obesity when diet and exercise have been unsuccessful. By modifying the digestive system, it helps patients lose significant weight and improve overall health. The success of this surgery depends not only on the surgical procedure but also on a comprehensive care plan involving a team of healthcare professionals.
To optimize outcomes, future research should focus on comparing different surgical techniques, understanding the role of multidisciplinary care, exploring the benefits of advanced technology, and addressing health disparities among patients.
Ultimately, metabolic surgery offers hope to many individuals struggling with obesity, and ongoing research will continue to improve its effectiveness and accessibility.
Conclusion: Embracing Hope and Health
While the immediate benefits of metabolic surgery are impressive, understanding the long-term effects is crucial. Researchers must focus on tracking weight loss, metabolic improvements, and potential complications over extended periods to provide comprehensive guidance for patients and healthcare providers.
Beyond clinical outcomes, it’s essential to consider the broader impact on patients’ lives. Factors such as overall quality of life, mental health, and satisfaction are equally important. A holistic approach will provide a more complete picture of metabolic surgery’s true value.
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10718334/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9951503/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7272689/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10805109/
- https://asmbs.org/patients/surgery-for-diabetes/
- https://asmbs.org/news_releases/new-studies-suggest-benefit-of-total-robotic-metabolic-and-metabolic-surgery-over-conventional-laparoscopy/