Imagine a Life Free from the Struggles of Obesity: Your Guide to Weight Loss Surgery
Imagine a life where every step feels like a struggle, and your breath hitches with every simple task. That’s the harsh reality for many living with severe obesity.
Struggling with obesity can be overwhelming, impacting daily life and long-term health. obesity-related comorbidities like heart disease, diabetes, and high blood pressure can significantly affect one’s quality of life. Weight loss surgery offers a lifeline to those battling not just the bulge, but a cascade of health problems that come with it.
It not only improves mobility by taking pressure off joints but also reduces the risk of associated health complications. For some, the most life-changing benefit is the effective management & control of type 2 diabetes, often happening soon after surgery.
Understanding Weight Loss Surgery
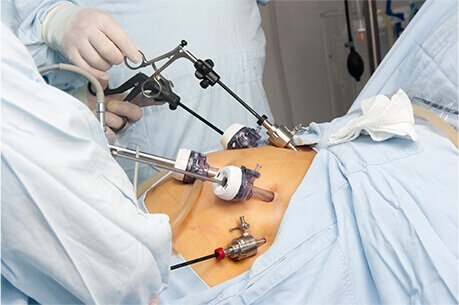
Weight loss surgery, also known as bariatric surgery, includes interventions such as gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy and offers a transformative approach to obesity management by modifying the anatomy of the stomach and small intestine. These interventions act on the body’s hormonal signaling system, influencing satiety (feeling of fullness) and hunger cues, while also impacting metabolic processes that regulate calorie intake. As a result, individuals experience a shift in their physiological makeup, facilitating significant and fast weight loss.
If you qualify for bariatric surgery, your weight loss surgeon and the healthcare team will determine the best surgical intervention for you and tailor a pre-surgery plan specific to your needs accordingly. Your pre-surgery preparation may involve:
Medical Checkups: Expect pre-operative lab tests and physical exams to establish your fitness levels for surgery.
Dietary and Medication Adjustments: You may receive instructions on what to eat and drink, and which medications (if any) need to be stopped or taken before surgery.
Exercise and Lifestyle Changes: Starting a physical activity program and quitting tobacco and alcohol might be crucial for a successful surgery and recovery.
Health Benefits of Weight Loss Surgery
Imagine shedding 70 to 80% of your excess weight and keeping it off for good!
Bariatric surgery offers impressive long-term success rates. Patients achieve substantial weight loss, shedding around 70 to 80% of their excess weight and keeping it off in the long term. Beyond the numbers, the impact is life-changing. Many report increased energy, reduced pain, and the ability to engage in activities they once struggled with. The rapid weight loss even triggers hormonal changes that further support weight management. Remember, consistency is key! Regular exercise and a healthy diet regimen after surgery play a crucial role in maintaining weight loss and newfound vitality.
Moreover, studies show a significant reduction in the risk of death from various conditions:
- Heart Disease: Patients see a remarkable 40% decrease in their risk of dying from heart-related issues.
- Diabetes: The risk of death from diabetes plummets by an impressive 92% after surgery.
- Cancer: The chances of succumbing to cancer also see a significant 60% drop.
Well-being and Quality of Life Improvements
Diet-induced weight loss often isn’t sufficient nor sustainable, so health complications associated with obesity tend to persist.
Bariatric surgery offers a significant transformation that extends far beyond just weight loss. While significant weight loss is a key benefit, the true magic lies in the overall health improvements it unlocks. Patients report a surge in energy, a brighter outlook, and a newfound confidence that empowers them to fully embrace life. Activities that may have once been difficult or avoided become accessible, leading to a more fulfilling lifestyle.
The positive impact doesn’t stop there. Bariatric surgery becomes a catalyst for adopting healthier habits, including better food choices and regular exercise. This ripple effect often extends to loved ones, creating a supportive and healthy environment within families. Ultimately, weight loss surgery empowers patients to take control of their health, not just for the present, but for the long term. It’s a testament to the power of modern medicine in promoting a healthier, longer, and more fulfilling life.
Who Should Consider Weight Loss Surgery?
If you are trying hard to lose weight and/or have been battling weight-related complications, you might be wondering if weight loss surgery is a viable option for you. It is important to understand that Weight Loss Surgery is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Here’s a breakdown of who might be a good candidate for bariatric or weight loss surgery:
- BMI above 32.5 kg/m2 with obesity-related co-morbidities
- BMI above 37.5 kg/m2 without co-morbidities.
- BMI > 30 kg/m2 with life-threatening obesity-related disorders like uncontrolled diabetes, cardiovascular disease/cardiomyopathy, and severe obstructive sleep apnoea.
- Patients motivated to lose weight and are committed to long-term follow-up.
- Patients who have unsuccessfully attempted conservative methods of weight loss in the past.
- Weight Loss Surgery is to be considered only between the ages of 18 – 65 years.
- Weight Loss surgery may be considered in patients more than 65 years old in case of severe obesity-related co-morbidities/disability.
- Weight Loss Surgery may be considered in patients < 18 years in special situations as recommended by a trained pediatrician/endocrinologist, or after attainment of puberty/completion of skeletal maturity.
Weight Loss surgery is a life-changing procedure, and the surgeon you choose plays a critical role in your safety, success, and overall experience. Here’s why selecting a right bariatric surgeon is crucial:
- Long-Term Support: A good bariatric surgeon offers comprehensive care beyond surgery. They will guide you through pre-operative education, support you during recovery, and provide long-term follow-up care. This includes nutritional counseling, managing potential side effects, and monitoring your overall health.
- Understanding Your Needs: Not all bariatric surgeries are the same. A skilled surgeon will take the time to understand your individual needs, medical history, and weight loss goals. They should discuss the various bariatric surgery options available (gastric bypass, sleeve gastrectomy, etc.) and explain the advantages and disadvantages of each concerning your specific situation.
- Experience Matters: Look for a surgeon who specializes in bariatric surgery and has a high volume of successful weight loss procedures under their belt. Experience translates to better surgical technique, improved efficiency, and a deeper understanding of potential complications and how to manage them.
Why Choose Dr. Atul Peters for Metabolic or Bariatric Surgery?
At Smart Cliniqs, we’re dedicated to your overall well-being, from the surgery itself to your post-operative recovery. Dr. Atul Peters, a renowned bariatric surgeon with over two decades of experience, has successfully performed numerous surgeries and is passionate about helping patients achieve their health goals. He leads comprehensive bariatric programs both locally and nationally, supported by a highly skilled team. Our global certification and active involvement in various National & International Surgical Societies underscores to our commitment to providing you with the best possible care.
Conclusion
While undergoing a weight loss surgery, you need to understand that results can vary, and long-term success requires a commitment from your side as well. Remember, obesity is a chronic condition, and additional treatments might be needed down the road. There are different surgical options with varying risks and benefits. Discuss these with your surgeon to see which weight loss surgery works for you.
References:
- Managing obesity (bomss.org)
- https://www.sages.org/
- https://asmbs.org/for-patients/
- https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/weight-management/bariatric-surgery
- Obesity & Metabolic Surgery Society of India – OSSI (theossi.com)
- Best Weight Loss Surgery in Delhi NCR, Weight Loss Treatment India (atulpeters.com)
- Bariatric surgery – Mayo Clinic