Mini Gastric Bypass vs Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass: Understanding Your Weight Loss Journey
Embarking on a weight loss journey is a deeply personal experience. As obesity rates continue to rise globally, many people are turning to surgical solutions to help achieve substantial weight loss and improve their overall health.
This blog post addresses this concern and offers a comprehensive overview of Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass (RYGB) and Mini Gastric Bypass, two popular weight loss surgeries. It discusses the procedures, benefits, and potential risks associated with each option. The article also explores the criteria for eligibility for bariatric surgery in India and offers guidance on choosing a qualified bariatric surgeon in Delhi. Ultimately, the goal is to empower individuals considering weight loss surgery to make informed decisions based on their specific needs and goals.
Introduction
When considering weight loss surgery, understanding the available options is crucial. Two common procedures, Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass (RYGB) and Mini Gastric Bypass, offer significant weight loss benefits but differ in their techniques and outcomes.
On average, people who undergo gastric bypass surgeries, lose 70 to 80% of excess body weight. However, it’s important to remember that these surgeries require a lifelong commitment.
This blog will delve into the details of 2 such procedures, helping you make an informed decision about which is best suited to your individual needs.
What is Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass (RYGB) Surgery?
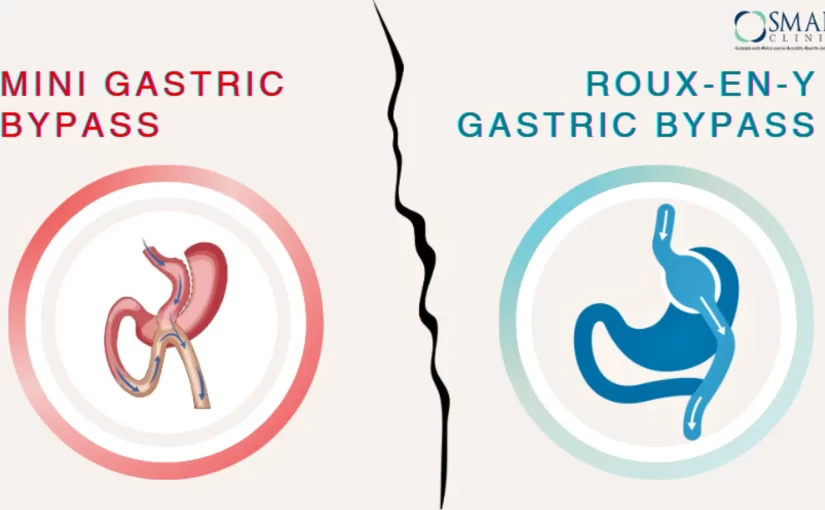
Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass (RYGB) is a more traditional weight loss surgery that involves creating a small stomach pouch and bypassing a portion of the small intestine. This rerouting of the digestive system leads to reduced food intake and absorption, resulting in significant weight loss.
How RYGB Works:
- Stomach pouch creation: The upper portion of the stomach, near the oesophagus, is stapled to create a small pouch that holds less food.
- Intestinal rerouting: The lower section is attached directly to the new stomach pouch, creating a pathway called the “roux limb.” The upper section of the small intestine, which carries digestive juices, is then attached further down the digestive tract, to the end of the roux limb. This allows food to bypass the lower stomach, the duodenum (the first part of the small intestine), and a portion of the small intestine itself.
- Reduced food intake and absorption: The rerouted digestive system limits the amount of food that can be consumed at once and reduces the absorption of nutrients.
Benefits of RYGB Surgery:
- Significant weight loss: Patients often experience substantial weight loss within the first year of surgery.
- Improved health outcomes: RYGB can address obesity-related health conditions such as diabetes, high blood pressure, and sleep apnea.
- Long-term weight loss maintenance: Many individuals who undergo RYGB surgery are able to maintain their weight loss over the long term.
What is Mini Gastric Bypass Surgery?
Mini Gastric Bypass, also known as one anastomosis gastric bypass, is a less invasive procedure compared to the traditional Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass. It involves creating a small stomach pouch to limit food intake and rerouting part of the small intestine to reduce nutrient absorption.
How Mini Gastric Bypass Works:
- Stomach pouch creation: Similar to RYGB, the surgeon makes your stomach smaller by stapling and reshaping it into a long, slender pouch.
- Direct connection: A new path is created for the food to pass through. A section of your small intestine is connected to the new stomach pouch. This bypasses the lower part of your stomach, the duodenum, and some of your small intestine.
- Reduced food intake and absorption: The rerouted digestive system limits the amount of food that can be consumed and reduces the absorption of nutrients.
Benefits of Mini Gastric Bypass Surgery:
- Potential Reversibility: Unlike some weight loss surgeries, Mini Gastric Bypass is potentially reversible due to its simpler design.
- Reduced risk of obesity-related comorbidities: Mini Gastric Bypass can help address other health conditions associated with obesity, such as high blood pressure and sleep apnea like in RYGB.
- Less restrictive: Mini Gastric Bypass may allow for a more flexible diet compared to RYGB.
Which Gastric Bypass Surgery is Right for You?
The decision between Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass and Mini Gastric Bypass depends on various factors, including:
- Individual health goals: Consider your desired level of weight loss and any specific health conditions you want to address.
- Medical history: Discuss any existing medical conditions or risk factors with your surgeon.
- Lifestyle factors: Consider your dietary habits, exercise routine, and overall lifestyle.
There are minor differences in these two procedures. With different advantages and disadvantages, the best outcome will depend by making an informed choice in consultation with your bariatric surgeon.
Who is Bariatric Surgery for?
- Bariatric/metabolic surgery should be considered a treatment option for acceptable Indian patients with a BMI ? 35 kg/m2, with/without the presence of any obesity-related co-morbidity.
- Bariatric/metabolic surgery should be considered a treatment option for acceptable Indian patients with a BMI ? 30 kg/ m2, in the presence of two or more obesity-related co-morbidities.
- Bariatric/metabolic surgery should be considered as a non-primary treatment option for acceptable Indian patients with a BMI ? 27.5 kg/ m2, with uncontrolled type 2 diabetes despite optimum medical management.
- Any bariatric/metabolic surgery for an Indian patient with a BMI < 27.5 kg/ m2 should be strictly performed under an experimental study protocol with prior ethics committee approval and informed consent from the patient.
- Bariatric/metabolic surgery should be considered as a treatment option for acceptable Indian patients with central obesity with a waist circumference ? 80 cm in females and ? 90 cm in males along with type 2 diabetes and other obesity-related co-morbidities.
- Bariatric/metabolic surgery may be advised as a treatment option for acceptable Indian patients who qualify for the above BMI criteria if they are ? 18 years of age. It may be advised as a treatment option to patients younger than 18 years of age under special circumstances with the approval of a multi-disciplinary team constituting a pediatrician, endocrinologist, dietician, psychologist, and a bariatric team including a bariatric surgeon. Attainment of puberty and completion of skeletal maturity must be taken into account for this patient population when considering the option of surgery.
- Bariatric/metabolic surgery should be advised as a treatment option for acceptable Indian patients who qualify for the above BMI criteria for patients up to 65 years of age. Bariatric/metabolic surgery may also be recommended for patients ? 65 years of age if they are medically fit, and the benefits of surgery outweigh the risks.
- All patients who are advised of bariatric/metabolic surgery as a treatment option should be motivated to enter a long-term weight management program and should be committed to life-long follow-up.
- Long-term weight management programs and follow-ups must be provided by all bariatric teams.
Choosing a Bariatric Surgeon in Delhi
It’s essential to consult with a qualified bariatric surgeon who can assess your individual needs and recommend the most appropriate procedure. A bariatric surgeon can provide personalized guidance, address your questions and concerns, and help you make an informed decision.
Ready to take the next step towards a healthier you?
Here’s a quick checklist to help you find the perfect fit:
- Experience and qualifications: Look for a surgeon with extensive experience in performing weight loss surgeries.
- Board certification: Ensure the surgeon is board-certified in bariatric surgery.
- Hospital affiliation: Consider the surgeon’s affiliation with reputable hospitals in Delhi.
- Patient reviews and testimonials: Read reviews and testimonials from previous patients to get a sense of the surgeon’s expertise and patient satisfaction.
Preparing for Weight Loss Surgery
If you decide to undergo weight loss surgery, it’s important to prepare for the procedure and the recovery process. This may involve:
- Making lifestyle changes: Adopting healthier eating habits and increasing physical activity can help you prepare for surgery and improve your overall health.
- Undergoing pre-operative evaluations: You may need to undergo various medical tests and evaluations to assess your suitability for surgery.
- Following pre-operative instructions: Your surgeon will provide specific instructions to follow before the procedure.
Recovery and Post-Operative Care
Recovery from weight loss surgery typically involves a hospital stay of several days, followed by a period of at-home recovery. During this time, you will need to follow your surgeon’s instructions for wound care, medication, and dietary restrictions.
Long-Term Follow-Up
After surgery, it’s important to attend regular follow-up appointments with your bariatric surgeon. These appointments will help monitor your progress, address any concerns, and ensure that you are receiving the necessary support for long-term weight loss maintenance.
Conclusion: Mini Gastric Bypass vs Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass
Both, Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass and Mini Gastric Bypass, surgeries offer significant potential for weight loss and improved health outcomes. By understanding the differences between these procedures and consulting with a qualified bariatric surgeon, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your unique needs and goals. Remember, the journey to a healthier you, begins with taking the first step and seeking the right guidance.